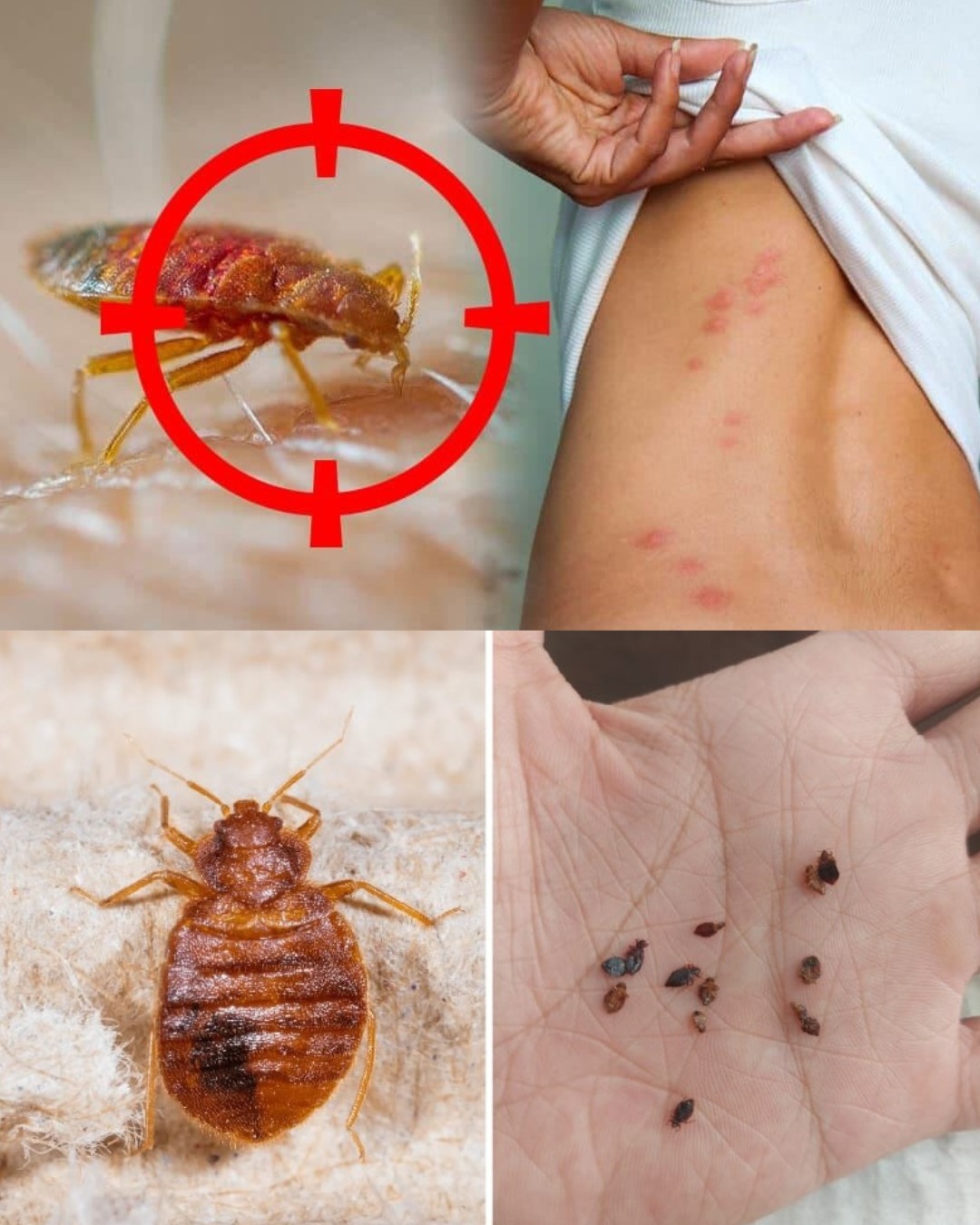
Bedbugs are tiny, blood-sucking insects that can quickly become a nuisance in homes, hotels, and other living spaces. Their presence can cause physical discomfort, emotional distress, and significant challenges in maintaining a peaceful living environment. Understanding how bedbugs live and knowing effective eradication methods are essential for any homeowner. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the biology of bedbugs, their habits, and a simple yet effective method for eradicating them from your home.
Understanding Bedbugs
What Are Bedbugs?
Bedbugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, reddish-brown insects that belong to the family Cimicidae. Adult bedbugs are approximately 4 to 5 millimeters long, roughly the size of an apple seed. They have flat, oval bodies, making it easy for them to hide in crevices and seams of furniture, mattresses, and bedding.
Life Cycle of Bedbugs
- Egg Stage: Female bedbugs lay eggs, typically in clusters of 10 to 50, in hidden locations. The eggs are tiny (about 1 millimeter) and white or translucent.
- Nymph Stage: After about a week, the eggs hatch into nymphs, which are smaller versions of adult bedbugs. Nymphs go through five molts before reaching adulthood, requiring a blood meal before each molt.
- Adult Stage: Adults can live for several months to a year, depending on conditions. They can survive for long periods without feeding, making them resilient pests.
Feeding Habits
Bedbugs primarily feed on human blood, usually at night when their hosts are asleep. They use specialized mouthparts to pierce the skin and draw blood, often causing itchy welts and allergic reactions.