Habitats
Bedbugs are expert hitchhikers, often traveling between locations via luggage, clothing, used furniture, or even on public transportation. They prefer warm environments and are commonly found in:
- Mattresses and box springs
- Bed frames and headboards
- Furniture seams and upholstery
- Baseboards and wall cracks
- Behind pictures and electrical outlets
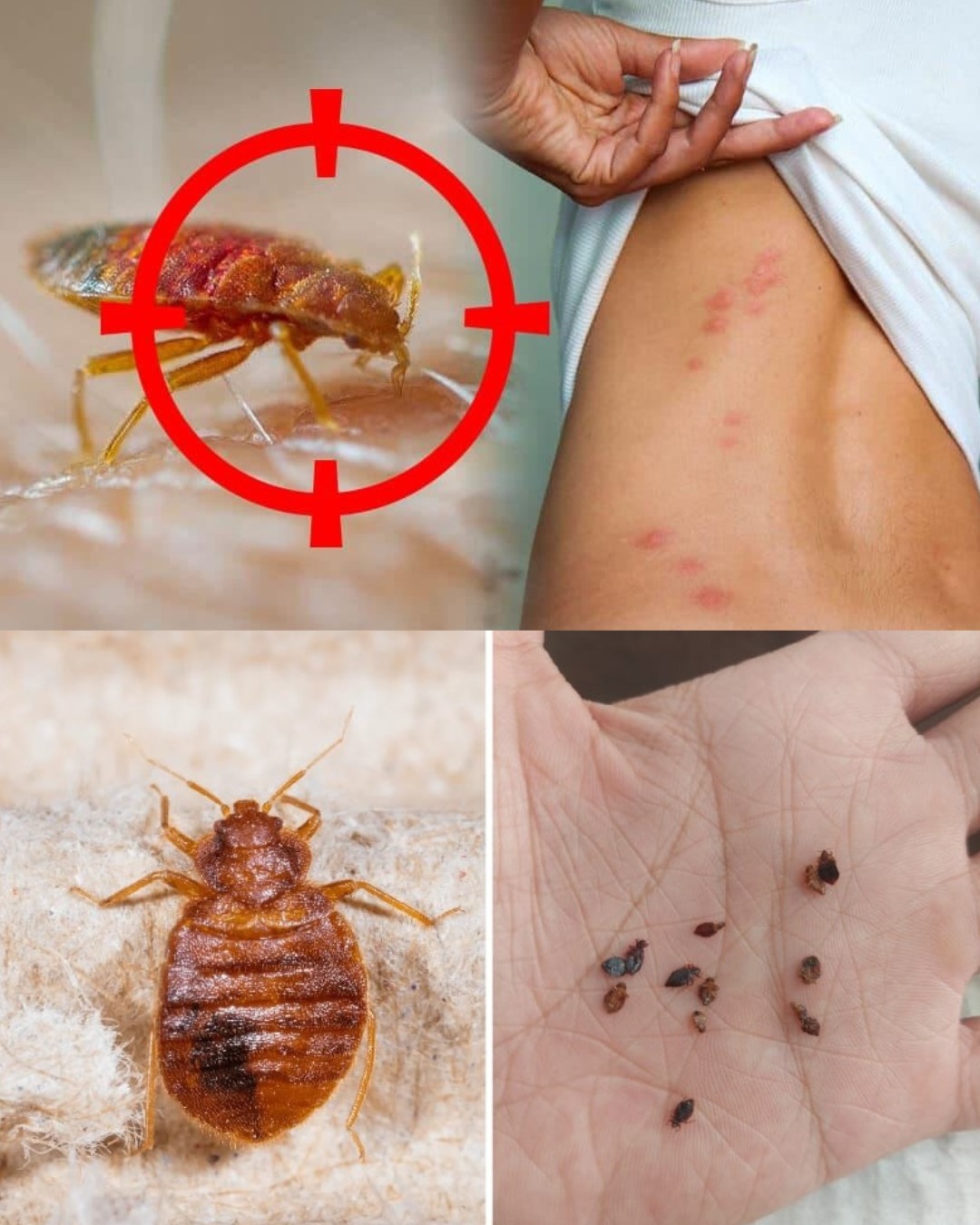
Signs of Bedbug Infestation
Recognizing the signs of a bedbug infestation is crucial for early detection. Look for:
- Bites: Itchy, red welts on the skin, often in a line or cluster.
- Exoskeletons: Shed skin from nymphs or adults.
- Fecal Spots: Small, dark spots on bedding or surfaces, indicating digested blood.
- Eggs: Tiny white eggs or egg casings in hidden areas.
- Odor: A sweet, musty smell in heavily infested areas.
How to Eradicate Bedbugs: A Simple Method
Eradicating bedbugs requires a systematic approach. One effective method involves a combination of thorough cleaning, heat treatment, and the application of diatomaceous earth.
Step 1: Preparation
Decluttering
- Remove Clutter: Eliminate unnecessary items in your home, especially around sleeping areas. This makes it easier to spot and treat bedbugs.
- Launder Fabrics: Wash all bedding, linens, and clothing in hot water (at least 120°F) and dry them on high heat for at least 30 minutes. This will kill any bedbugs and their eggs.
Step 2: Inspect and Treat Affected Areas
Thorough Inspection
- Check Bedding: Examine mattresses, box springs, and bed frames for signs of bedbugs. Look for fecal spots, shed skins, and actual insects.
- Inspect Furniture: Check seams, cushions, and crevices of sofas and chairs, as well as behind and under furniture.
Vacuuming
- Vacuum Thoroughly: Use a vacuum with a HEPA filter to vacuum infested areas, including carpets, rugs, and baseboards. Pay special attention to seams and crevices.
- Dispose of Vacuum Contents: Seal the vacuum bag in plastic and dispose of it immediately outside your home.
Step 3: Heat Treatment
Bedbugs are highly susceptible to heat, making heat treatment an effective eradication method.
How to Use Heat
- Identify Affected Areas: Focus on areas where bedbugs have been found, including mattresses, furniture, and luggage.
- Use a Steamer: A handheld steamer can be effective for treating surfaces. Ensure the steamer produces steam at a minimum of 120°F.
- Steam Application: Slowly move the steamer over affected areas, ensuring to hit seams, folds, and hidden spots. Keep the nozzle close to the surface but avoid direct contact.
Step 4: Application of Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous earth (DE) is a natural powder made from the fossilized remains of tiny, aquatic organisms called diatoms. It is effective against bedbugs and other pests.
How to Apply DE
- Choose Food-Grade DE: Ensure you use food-grade diatomaceous earth, which is safe for indoor use.
- Apply Thin Layers: Sprinkle a thin layer of DE in areas where bedbugs are found, including around beds, along baseboards, and in cracks and crevices.
- Leave for Several Days: Allow the DE to remain undisturbed for several days to maximize its effectiveness. After this period, vacuum up the powder.
Step 5: Reassessment and Follow-Up
Monitor for Signs
- Regular Inspections: Continue to monitor your home for signs of bedbugs after treatment. Check bedding, furniture, and luggage regularly.
- Repeat Treatments: If you observe any signs of bedbugs, repeat the cleaning, heat treatment, and DE application as necessary.
Step 6: Prevention
Preventing future infestations is crucial in maintaining a bedbug-free home.
- Protective Covers: Use encasements on mattresses and box springs to prevent bedbugs from entering or escaping.
- Regular Cleaning: Maintain a routine of cleaning and vacuuming your home, paying special attention to sleeping areas.
- Be Cautious When Traveling: Inspect hotel rooms for signs of bedbugs before settling in. Keep luggage elevated and away from beds and furniture.